背景介紹
業務介紹
在某學習App瀏覽文章,客戶端會將瀏覽的文章信息上傳到服務端,服務端將瀏覽信息最終存儲到HBase;
在某學習APP首頁點擊【我的】->【歷史】,會展示用戶瀏覽文章的歷史記錄。
技術介紹
服務端的服務是【閱讀歷史離線服務】,從metaq消費用戶閱讀文章的信息,解析、處理相關業務邏輯,最后存儲到HBase。
問題現象
ECS監控
兩臺機器【xx-xxxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-6、xx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-xxx-1】在早高峰的時候Load很高,CPU使用率正常。

metaq監控
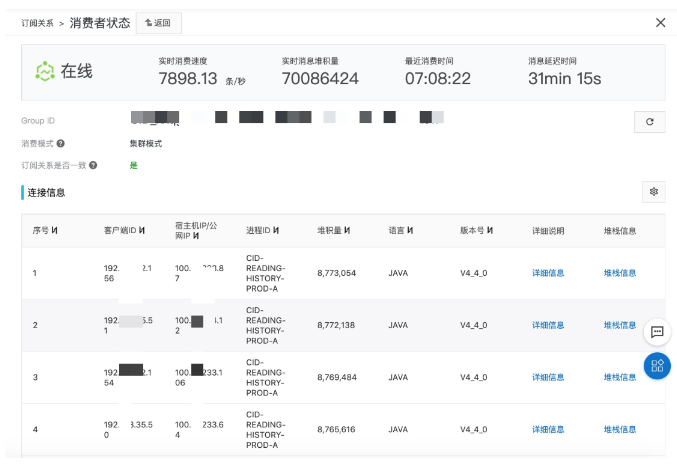
造成消息消費的慢,每天早上都有大量消息堆積,導致用戶看不到自己的閱讀歷史。
問題分析
基本情況
【閱讀歷史離線服務】共有x臺ECS,每臺ECS配置是8c16g。其中x臺機器正常,2臺機器不正常。
排查思路
找不同
分析不正常機器與正常機器有哪些差異:對比了【應用程序版本】、【應用程序配置】、【JVM配置參數】、【JDK版本】、【操作系統版本】,發現【JDK版本】不一致。
正常機器:
openjdk version "1.8.0_171"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_171-b10)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.171-b10, mixed mode)
異常機器:
openjdk version "1.8.0_222"
OpenJDK Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_222-b10)
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.222-b10, mixed mode)
到此初步定位不同機器運行狀態不一致的現象是由于【JDK版本】不一致造成的,所以將【問題機器的JDK版本】替換為【正常機器的JDK版本】問題就可以解決了。
定位問題代碼
但是問題的根因還需要嘗試排查一下,既然是【JDK版本】不一致造成的,那么會不會是【1.8.0_222】這個版本中有BUG,剛好我們寫的程序觸發了這個BUG?
所以接下來需要弄清楚程序運行過程中執行了哪些業務邏輯、這些業務邏輯涉及到了哪些JDK API,直接想到的工具是arthas profiler,下面是抓到的熱點方法。
通過對比【異常機器】與【正常機器】的熱點方法,發現Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()很可疑:
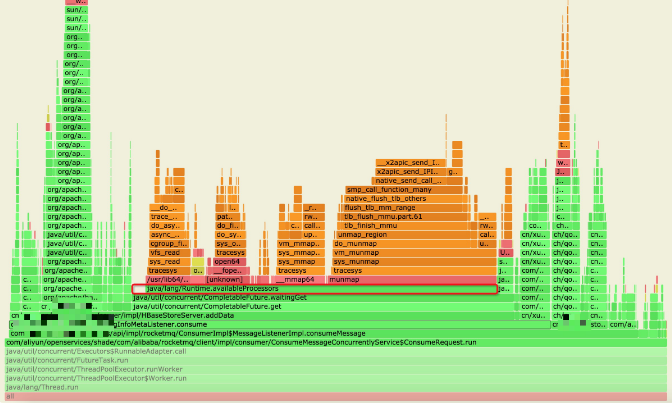
業務相關代碼:
CompletableFuture<Result> completableFuture = //業務邏輯,調用hbase-client中api
completableFuture.whenCompleteAsync((result, t) -> {
//業務邏輯處理
}, Pool.getSubmitPool()).exceptionally((t) -> {
//業務邏輯處理
}).get();
CompletableFuture相關代碼:
/**
* Waits if necessary for this future to complete, and then
* returns its result.
*
* @return the result value
* @throws CancellationException if this future was cancelled
* @throws ExecutionException if this future completed exceptionally
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
*/
public T get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException {
Object r;
return reportGet((r = result) == null ? waitingGet(true) : r);
}
/**
* Returns raw result after waiting, or null if interruptible and
* interrupted.
*/
private Object waitingGet(boolean interruptible) {
Signaller q = null;
boolean queued = false;
int spins = -1;
Object r;
while ((r = result) == null) {
if (spins < 0)
spins = (Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() > 1) ?
1 << 8 : 0; // Use brief spin-wait on multiprocessors
else if (spins > 0) {
if (ThreadLocalRandom.nextSecondarySeed() >= 0)
--spins;
}
else if (q == null)
q = new Signaller(interruptible, 0L, 0L);
else if (!queued)
queued = tryPushStack(q);
else if (interruptible && q.interruptControl < 0) {
q.thread = null;
cleanStack();
return null;
}
else if (q.thread != null && result == null) {
try {
ForkJoinPool.managedBlock(q);
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
q.interruptControl = -1;
}
}
}
if (q != null) {
q.thread = null;
if (q.interruptControl < 0) {
if (interruptible)
r = null; // report interruption
else
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
postComplete();
return r;
}
猜測驗證
public class Processors {
public static void main(String []args) {
int availableProcessors = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
System.out.println("Available Processors: " + availableProcessors);
for(int i = 0;i < availableProcessors;i++){
Thread t = new Thread(()-> {
while (true){
try {
int ps = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors();
Thread.sleep(1L);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
t.start();
}
}
}
將驗證代碼在【JDK版本】為【1.8.0_222】的機器上運行,隨即復現了線上問題。
定位根因
那么【1.8.0_222】與【1.8.0_171】版本在Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()的實現上有什么差別呢?【1.8.0_222】增加了容器環境的邏輯,比【1.8.0_171】復雜了很多。
最后我們看看在
https://bugs.openjdk.JAVA.NET/的解釋吧。

總結:
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()在不同JDK版本上的實現是沒有問題的,
CompletableFuture.waitingGet在【1.8.0_222】版本上,沒有測試到Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()對性能的影響,導致了性能問題。
解決方法
openjdk在1.8.0_191~1.8.0_222之間的版本都存在問題,換成1.8.0_191之前,或1.8.0_232及以后的版本可以。
問題根因
CompletableFuture.get()的實現方式在一些jdk版本存在缺陷,
詳情見:[JDK-8227018] CompletableFuture should not call
Runtime.availableProcessors on fast path - Java Bug System






