1、console.log輸出
console.log(([][[]]+[])[+!![]]+([]+{})[!+[]+!![]])
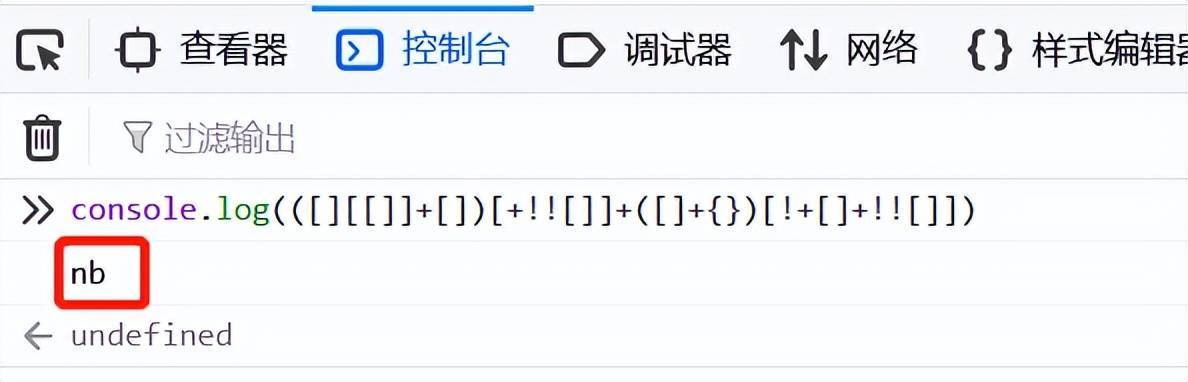
2、優(yōu)雅的取隨機(jī)字符串
Math.random().toString(16).substring(2)
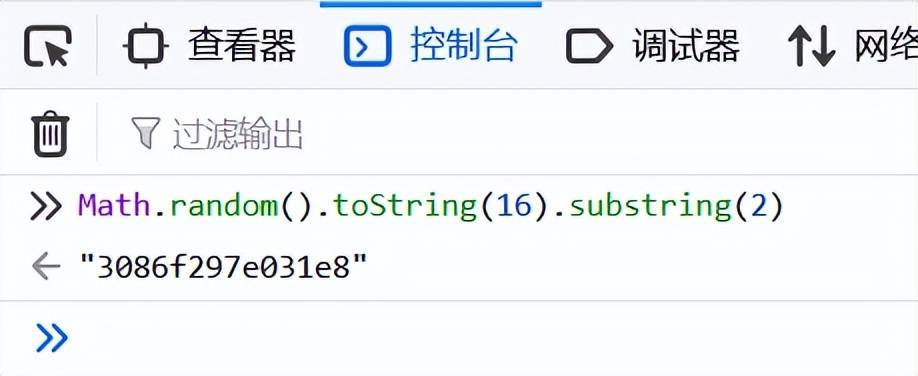
3、if比較
["toString"]() === "10"
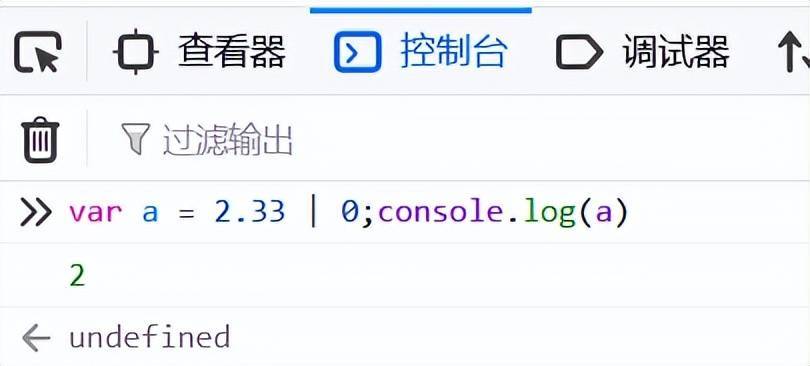
4、優(yōu)雅的取整
var a= 2.33 | 0
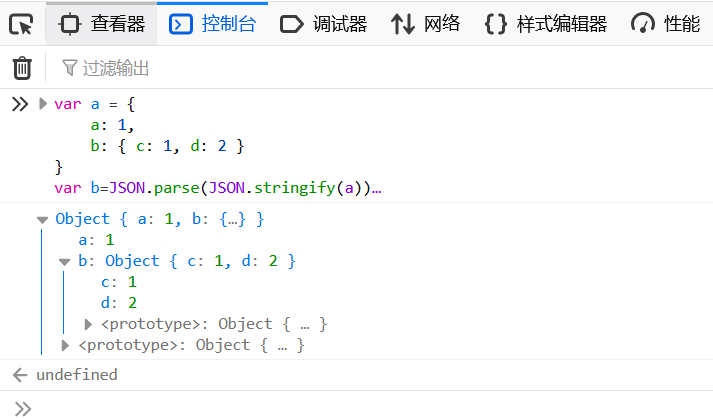
5、標(biāo)準(zhǔn)JSON的深拷貝
var a = {
a: 1,
b: { c: 1, d: 2 }
}
var b=JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(a))
console.log(b)
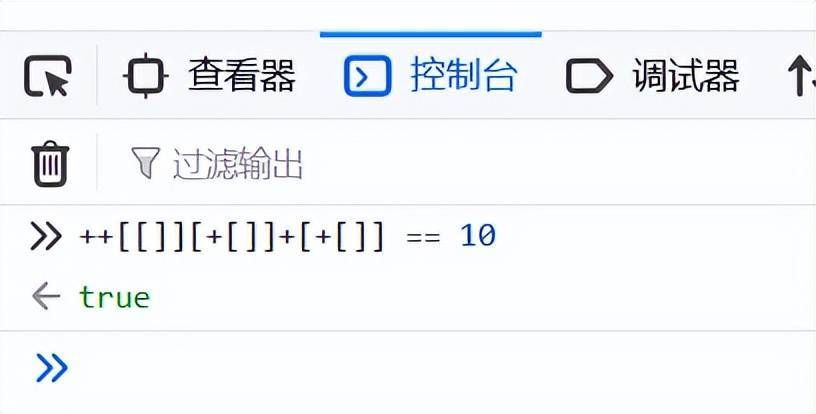
6、相等
++[[]][+[]]+[+[]] == 10
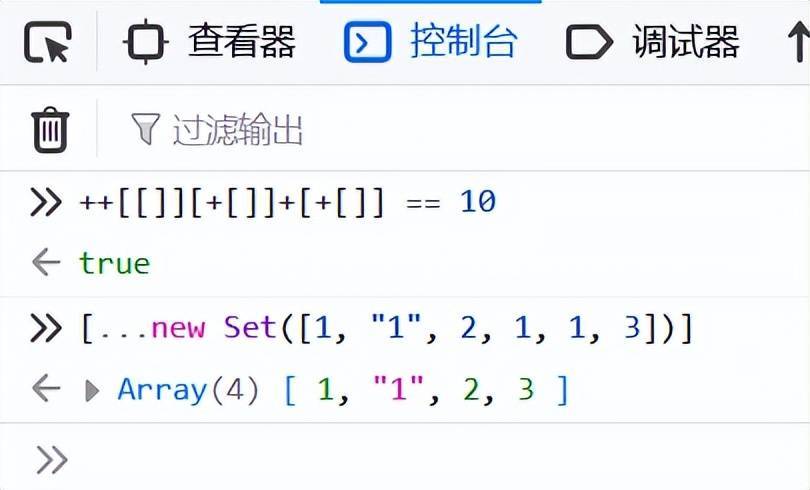
7、數(shù)組去重
[...new Set([1, "1", 2, 1, 1, 3])]
8、實(shí)現(xiàn)一個(gè)長度為m(6)且值都n(8)的數(shù)組
Array(6).fill(8)

9、取出一個(gè)數(shù)組中的最大值和最小值
var numbers = [5, 458 , 120 , -215 , 228 , 400 , 122205, -85411];
var maxInNumbers = Math.max.Apply(Math, numbers);
var minInNumbers = Math.min.apply(Math, numbers);
console.log(maxInNumbers,minInNumbers);

10、高逼格的Function
var f = new Function('a', 'alert(a)'); f('jshaman');
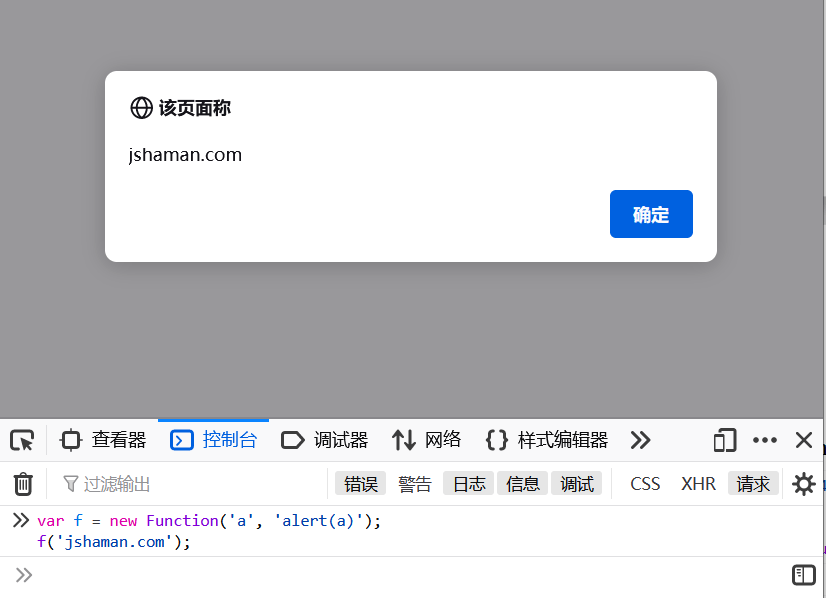
Function構(gòu)造函數(shù)接受的參數(shù)中,第一個(gè)是要傳入的參數(shù)名,第二個(gè)是函數(shù)內(nèi)的代碼。
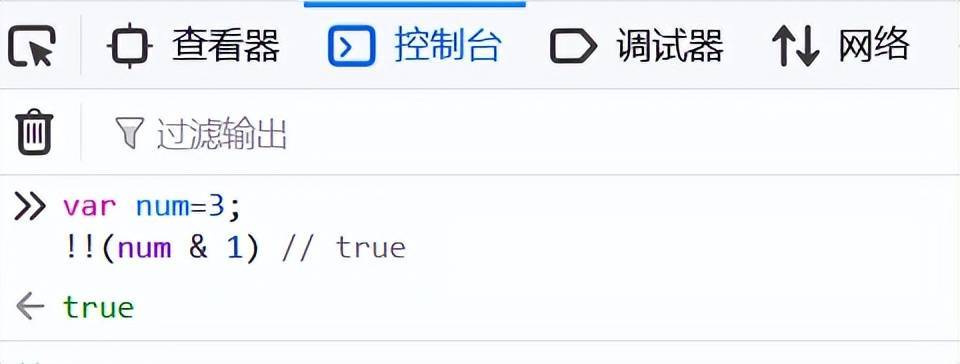
11、判斷奇偶數(shù)
對一個(gè)數(shù)字 &1可以判斷奇偶數(shù),負(fù)數(shù)也同樣適用, num&1
var num=3;
!!(num & 1) // true
!!(num % 2) // true
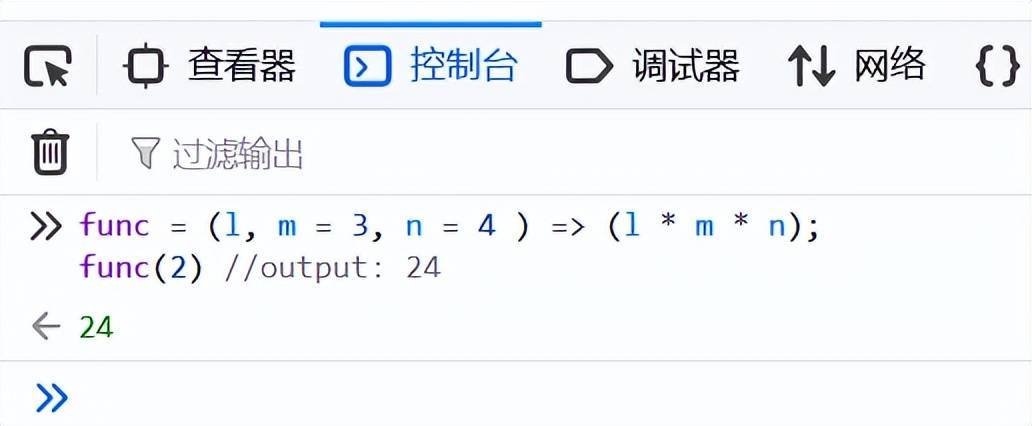
12、函數(shù)默認(rèn)值
func = (l, m = 3, n = 4 ) => (l * m * n);
func(2) //output: 24
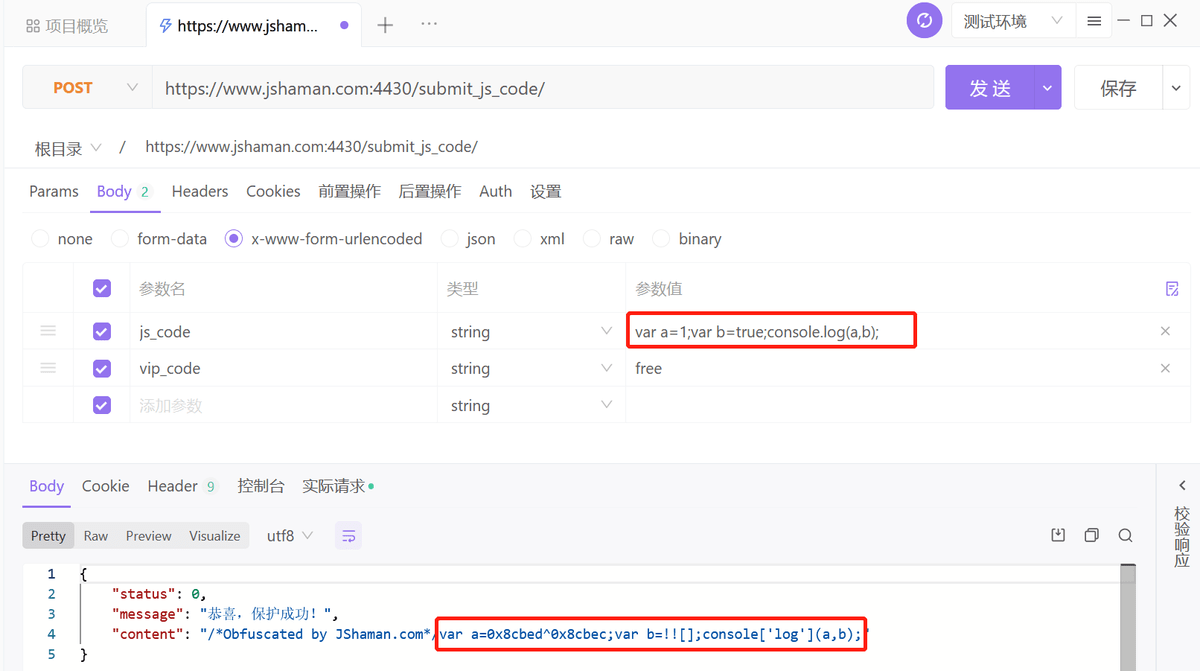
13、JS代碼混淆加密
var a=1;
var b=true;
console.log(a,b);
調(diào)用JShaman接口對JS代碼進(jìn)行混淆加密:
14、字符串比較時(shí)間先后
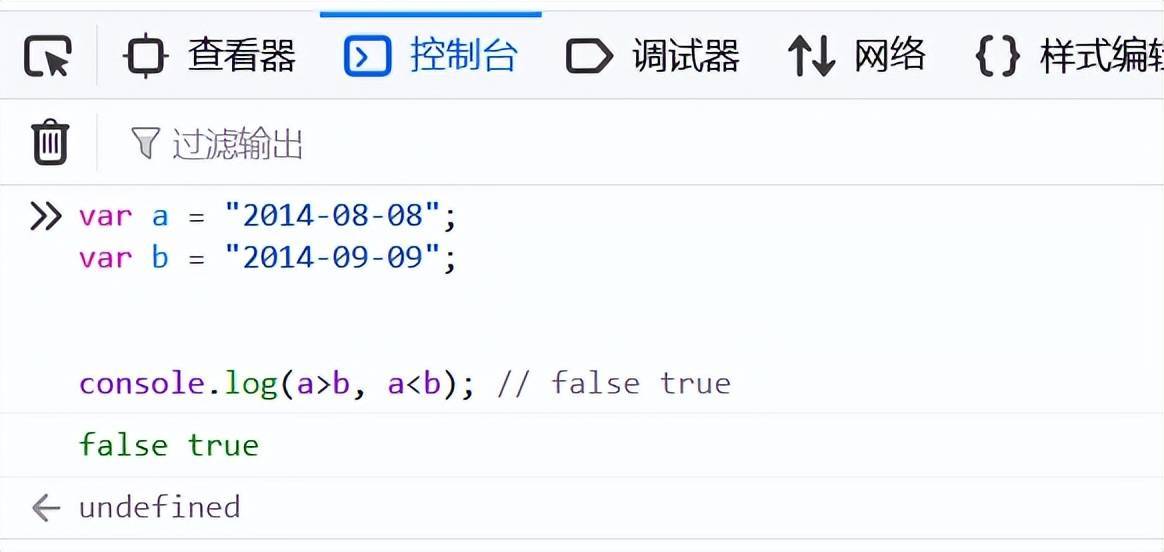
var a = "2014-08-08";
var b = "2014-09-09";
console.log(a>b, a<b); // false true
15、使用解構(gòu)來交換參數(shù)數(shù)值
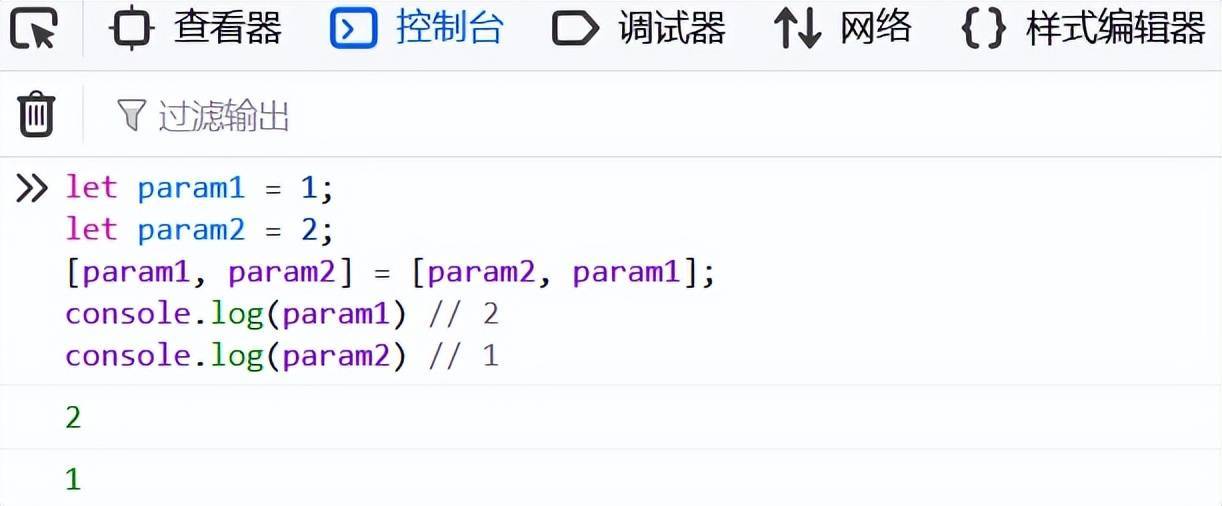
有時(shí)候你會將函數(shù)返回的多個(gè)值放在一個(gè)數(shù)組里。我們可以使用數(shù)組解構(gòu)來獲取其中每一個(gè)值。
let param1 = 1;
let param2 = 2;
[param1, param2] = [param2, param1];
console.log(param1) // 2
console.log(param2) // 1
16、使用解構(gòu)刪除不必要屬性
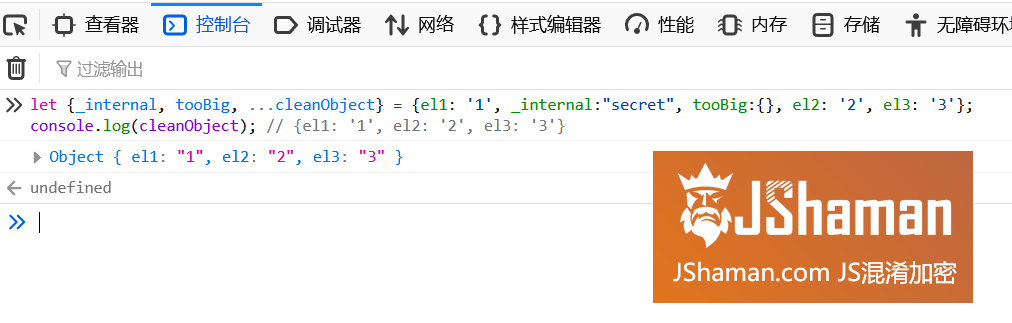
有時(shí)候你不希望保留某些對象屬性,也許是因?yàn)樗鼈儼舾行畔⒒騼H僅是太大了(just too big)。你可能會枚舉整個(gè)對象然后刪除它們,但實(shí)際上只需要簡單的將這些無用屬性賦值給變量,然后把想要保留的有用部分作為剩余參數(shù)就可以了。
下面的代碼里,我們希望刪除_internal和tooBig參數(shù)。我們可以把它們賦值給internal和tooBig變量,然后在cleanObject中存儲剩下的屬性以備后用。
let {_internal, tooBig, ...cleanObject} = {el1: '1', _internal:"secret", tooBig:{}, el2: '2', el3: '3'};
console.log(cleanObject); // {el1: '1', el2: '2', el3: '3'}
17、在函數(shù)參數(shù)中解構(gòu)嵌套對象
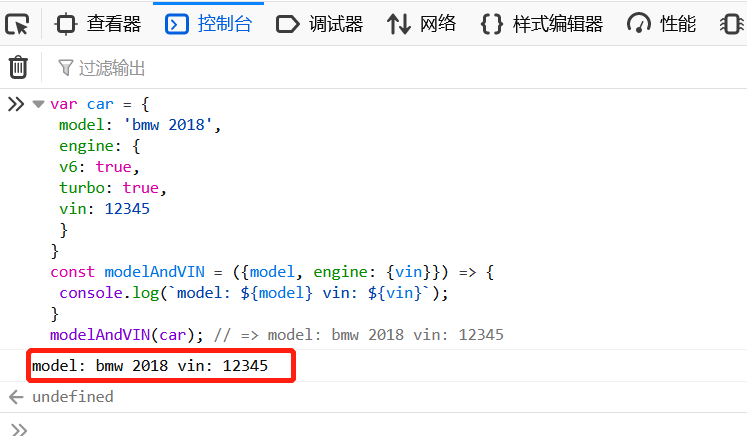
在下面的代碼中,engine是對象car中嵌套的一個(gè)對象。如果我們對engine的vin屬性感興趣,使用解構(gòu)賦值可以很輕松地得到它。
var car = {
model: 'bmw 2018',
engine: {
v6: true,
turbo: true,
vin: 12345
}
}
const modelAndVIN = ({model, engine: {vin}}) => {
console.log(`model: ${model} vin: ${vin}`);
}
modelAndVIN(car); // => model: bmw 2018 vin: 12345
18、帶有多個(gè)條件的 if 語句
把多個(gè)值放在一個(gè)數(shù)組中,然后調(diào)用數(shù)組的 includes 方法。
// bad
if (x === "abc" || x === "def" || x === "ghi" || x === "jkl") {
//logic
}
// better
if (["abc", "def", "ghi", "jkl"].includes(x)) {
//logic
}
19、條件查找簡化
如果我們要基于不同的類型調(diào)用不同的方法,可以使用多個(gè) else if 語句或 switch,但有沒有比這更好的簡化技巧呢?其實(shí)是前面的 switch 簡化方式一樣!
// bad
if (type === "test1") {
test1();
} else if (type === "test2") {
test2();
} else if (type === "test3") {
test3();
} else if (type === "test4") {
test4();
} else {
throw new Error("Invalid value " + type);
}
// better
var types = {
test1,
test2,
test3,
test4,
};
types[type] && types[type]();
20、跨行字符串
// bad
const data =
"abc abc abc abc abc abcnt" + "test test,test test test testnt";
// better
const data = `abc abc abc abc abc abc
test test,test test test test`;
21、順序執(zhí)行 promise
如果你有一堆異步或普通函數(shù)都返回 promise,要求你一個(gè)接一個(gè)地執(zhí)行,怎么辦?
async function getData() {
const promises = [fetch("url1"), fetch("url2"), fetch("url3"), fetch("url4")];
for (const item of promises) {
// 打印出promise
console.log(item);
}
// better
for await (const item of promises) {
// 打印出請求的結(jié)果
console.log(item);
}
}
22、打亂數(shù)組
const list = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9];
list.sort(() => {
return Math.random() - 0.5;
});
// 輸出
(9) [2, 5, 1, 6, 9, 8, 4, 3, 7]
// Call it again
(9) [4, 1, 7, 5, 3, 8, 2, 9, 6]

23、將Object屬性轉(zhuǎn)成屬性數(shù)組
const obj = { a: 1, b: 2, c: 3 };
Object.entries(obj);
// 輸出
(3) [Array(2), Array(2), Array(2)]
0: (2) ["a", 1]
1: (2) ["b", 2]
2: (2) ["c", 3]
length: 3
Object.keys(obj);
(3) ["a", "b", "c"]
Object.values(obj);
(3) [1, 2, 3]







